Legionella disease: hot & cold water tanks
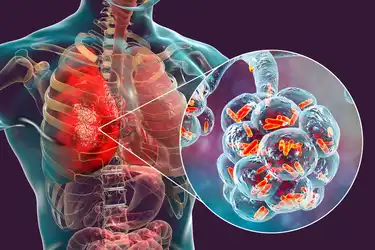
Legionella disease is a serious and potentially life-threatening illness. This will be caused by exposure to water contaminated with Legionella bacteria.
We will discuss what you need to know about this dangerous disease!
How it is contracted, the symptoms of infection from legionella, and steps that should be taken to prevent contracting the illness. We will discuss the dangers of legionnaires disease in the plumbing systems.
What is Legionnaires disease?
Legionella bacteria is commonly found in water but can be found at higher levels as a result of warmer, or cooler, temperatures. The bacteria multiply in hot and cold water storage tanks when the temperature is between 20-45°C.
The bacterium will survive in low temperatures and are inactive below 20°C, and will die at 60°C.
The risk of the legionella bacteria
The dangers of legionella disease are very common in the plumbing industry. The disease is a deadly type of pneumonia that contracted by inhaling droplets containing live bacteria. When inhaled, these droplets from the water outlet and air conditioning can cause legionella disease. Common areas are hot and cold water outlets, shower rooms, spas and fitness centres where.
How does it spread
The bacterium can found in the water tank that poses the biggest threat is Legionella bacteria pneumonia.
Water supplies can carry the bacteria, but they won’t multiply in cold temperatures. When the bacterium gets inside the water heater it starts to multiply and it can spread through the plumbing system. While you take a shower you can bread in the bacterium. Bathing is one of the main ways people get infected with Legionnaire’s disease.
That’s why it is so important to maintain the hot water cylinder temperatures over 60°C, where the bacteria will die.
Signs and symptoms of the legionnaires’ disease
In rare cases, patients have a headache, high fever and muscle ache. Some people might also experience chest pains while breathing.
Other symptoms include fever, dry cough, muscle aches, loss of energy, chest pain, chronic respiratory and kidney disease. If Legionnaires disease is caught in time it can be treated.
Prevention Tips and Tricks
Using temperature control is one way to prevent legionella from forming in your hot and cold water systems.
Every household hot water cylinder has a thermostat that controlling the temperatures in the cylinder and set to 60°C.
When you turn on the hot water and only find that it is lukewarm, your cylinder thermostat may have broken. It is time to call our plumber immediately who can investigate the issues.
How do you prevent legionella growth?

- Monitor the temperatures of your hot water cylinder and store the water over 60°C. The bacterium will survive low temperatures.
- Keep AC unit filters clean so that bacteria don’t have access to oxygen, which it needs for growth.
- Ensure there is no stagnant lukewarm water in your home.
- The cold water should be stored below 20°C.
- Never leave a dead leg on the pipework. Is called dead leg where the water is not moving through the pipe, and in stagnant water, the bacteria will grow.
- Check your cylinder at least once a month.
- Keep your plumbing system clean. Descale your showerheads and hoses. If can book a plumber who can wash out your cold water systems and hot water cylinder do it.
- You cant take a shower at 60°C, but the thermostatic mixer valves in the bathroom mixing the water to a desirable temperature.
Prevent hot and cold water stagnation and dead leg

When the water isn’t flowing well, it becomes stagnant and creates an environment where the bacterium will grow.
Water flow can be challenging to inspect. Knowing where stagnant water may accumulate can save your building from the spread of the bacterium.
How can you prevent bacterial growth in hot and cold water systems?
1.Your plumber has to design water systems that comply with the WRAS health and safety regulations.
2.Don’t leave any dead leg on the pipework.
3.Keep the pipework short.
4.Hot and cold water cylinders need to meet the regulations.
5.Insulate your pipework and storage water tanks and don’t forget to put on the cold water tank cover.
Other methods can be used for preventing the disease
Check your hot and cold water systems regularly that you have the appropriate temperatures. Book a plumber who can carry out a risk assessment, take water samples and analyse the bacterial growth.
In a bigger water system, you can also use silver, copper ionisation and biocide/chemical treatments. The chlorine dioxide will kill the bacterium. Every month, legionella control monitoring should be carried out. The microbiological count in water should be less than 103-104.
Frequently Asked Questions About Legionella bacteria
Q: Can Legionella grow in pipes?
Yes especially in dead legs where the water not moving. Minimise the unused pipework, keep your plumbing water system clean, and descale the showerheads.
Q: Where is Legionnaires infection most common?
The bacterium can be found everywhere in the world. The bacterium can be found in the most common areas, such as rivers, lakes, and pools.
Q: How does Legionella get into the water supply?
The bacterium can be found in the water supply but under 20°C they won’t grow. If reaches the storage cylinder it starts to grow if the water is not heated above 60degrees Celsius
Q: What is the most common way of contracting Legionnaires disease?
Usually, people get infected by inhaling the bacterium from water droplets while they take showers.
Q: Can Legionella survive in chlorinated water?
Yes. The bacterium is resistant to water treatments and will die at high temperatures.
Q: Can you get Legionnaires disease from tap water?
Yes, you can if the water is not kept above 60 degrees Celsius in the cylinder. You can breed in the bacterium droplets while you using the tap.
Q: Can you get Legionnaires infection from a shower?
The showerhead is the best place where the bacterium can be found. The bacterium will be dispersed in water droplets.
Q: How long does Legionella take to develop in water?
If the hot water is kept between 20-45°C in the storage tank, the bacterium can grow in 2-10 days.
Q: How often should showerheads be cleaned and disinfected?
Showerheads need to be disinfected every three months to prevent bacterium growth.
Q: Can you get legionella from cold water?
Yes, you can get infected. The bacterium can also be found in cold water systems. But they only grow if the temperature is between 20 – 45 °C. Under 20°C the bacterium go into hibernation.
Q: What happens if you drink water with Legionella?
If the water is infected and you cough or choke while you drinking and the water gets to your lungs, you can get infected.
Q: How do you get rid of bacterial Legionella?
If you return from holiday make sure to reheat your hot water cylinder above 60C before starting to use it. The bacterium will die at this high temperature.
Q: Can you do your own Legionella risk assessment?
You can perform the test yourself if you purchase a kit. But only expert plumbers know how to control legionella bacteria in your plumbing and water systems.
Do you need a plumber for your immersion heater replacement?
The post Legionella disease: hot & cold water tanks appeared first on MML Plumbing Ltd.
from MML Plumbing Ltd https://ift.tt/3xzOH66
via IFTTT


No comments:
Post a Comment